Meaning of "qudi" in Music
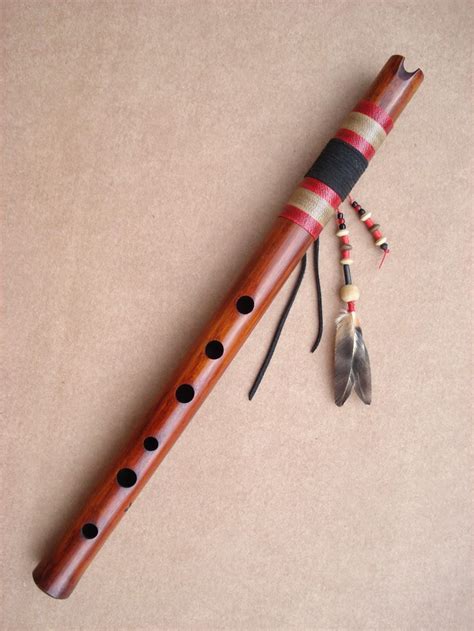
In the context of music, "qudi" refers to a type of Chinese transverse flute. The dizi, also known as di or hengdi, has various varieties, including the qudi and bangdi. The dizi is a major instrument in Chinese folk music, Chinese opera, and the modern Chinese orchestra. It is widely used and has been popular among the Chinese common people due to its simplicity and portability.
The qudi is one of the prevalent types of dizi. It is pitched a fourth or fifth lower than the bangdi, another type of dizi. The qudi is the lead melodic instrument in kunqu opera and is also used in other forms of Chinese music, such as Jiangnan sizhu ).
Please let me know if there's anything else I can help you with!
CLASSIFICATION: Aerophone, End-blown flute, Wind instrument – Western Equivalent – flute
HISTORY: The qudi appeared as early as in the Zeng Hou Yi tomb of the Warring States (403-221 BCE). The origin is from Suzhou city and is often used to accompany Kunqu opera.
PHYSICAL DESCRIPTION: The qudi is made of bamboo, and is around 55 cm in length. Similar to the flute, it has a mouthpiece, 6 open finger holes, and several auxiliary finger holes. It is slightly larger than the bangdi.
SOUND PROPERTIES: The qudi produces a rounded and rich sound similar to the bangdi, only pitched lower. The tone is pure and mellow, making it suitable for expressing delicate and understated moods.
RANGE: The range of the qudi is F4 to A flat5.
Similar Chinese instruments include: bangdi (piccolo); gudi (flute); qudi (flute); dizi (transverse flute); di (transverse flute); xiao (vertical flute); dong xiao (same as xiao).







Leave a Reply