Meaning of Mensural Notation in Music
Mensural notation is a musical notation system that was used for polyphonic European vocal music from the late 13th century until the early 17th century. The term "mensural" refers to the ability of this system to describe precisely measured rhythmic durations in terms of numerical proportions between note values. It was developed as a method to notate complex rhythms beyond the possibilities of previous notation systems, such as neumes.
The name "mensural notation" is inspired by the terminology used by medieval theorists, who referred to the rhythmically defined polyphonic music of their age as "musica mensurata" or "cantus mensurabilis". This distinguished it from Gregorian plainchant, which had its own older system of neume notation.
Mensural notation was primarily used for compositions in the tradition of vocal polyphony, while plainchant retained its own system of neume notation throughout the period. However, some purely instrumental music could also be written in various forms of instrument-specific tablature notation.
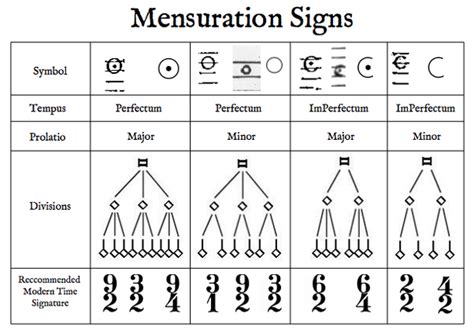
The system of mensural notation evolved over time, reaching its classical development after 1450. It was based on a single underlying musical pulse and divisions of time, including modus (division of the longa into two or three breves), tempus (division of the breve into two or three semibreves), and prolatio (division of the semibreve into two or three minima). Time signatures were used to indicate tempus and prolatio.
Overall, mensural notation played a significant role in the development of musical notation and allowed for the precise representation of complex rhythms in polyphonic music during the medieval and Renaissance periods.
References:
A system of notation established around 1260, remaining in use until about 1600. Initially, the three principal note values in use were the long, breve, and semibreve. The long was equal to three breves, and the breve equal to three semibreves. An additional fourth note, duplex long, was equal to two longs. By the 14th century, the minim was added and by the 15th century, the semiminima and fusa were also added.
In Mensural Notation, several notes can be combined together to form ligatures. In a ligature, the relationship between any two adjacent notes can be either triple (3) or duple (2). The relationship between the long and breve is the modus, and if the modus is triple (three breves to the long), then it is major. A duple modus (two breves to the long), is said to be minor. Similarly, the relationship between the breve and semibreve is the tempus, and if the tempus is triple (three semibreves to the breve), then it is perfect. A duple tempus (two semibreves to the breve), is said to be imperfect. Finally, the relationship between the semibreve and minim is the prolatio, and if the prolatio is triple (three minims to the semibreve), then it is major. A duple prolatio (two minims to the semibreve), is said to be minor.
In addition, you can familiarize yourself with the terms:
- [English] notation






Leave a Reply