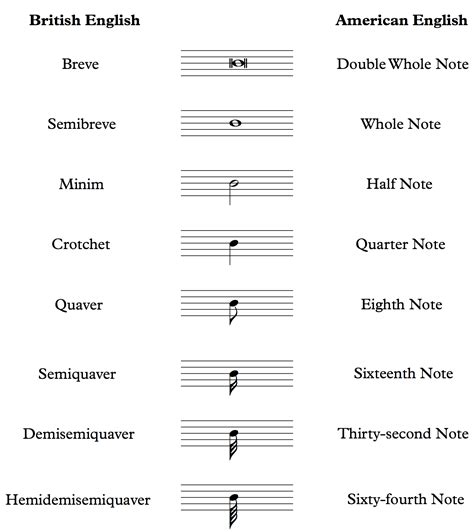
Meaning of T. Sax in Music
In music, "T. Sax" refers to the tenor saxophone. The tenor saxophone is a member of the saxophone family and is pitched in the key of B♭. It is larger than the alto saxophone and smaller than the baritone saxophone. The tenor saxophone is commonly used in various genres of music, including jazz, rock, and pop. It has a rich and expressive sound and is often featured in solos and improvisations.
An abbreviation for tenor saxophone.
In addition, you can familiarize yourself with the terms:
- [Abbreviation] tenor sax
- [Abbreviation] ten. sax
- [English] tenor saxophone
- [French] saxophone ténor (m)
- [German] Tenorsaxophon (n)
- [Italian] sassofono tenore (m)
- [Spanish] saxofón tenor (m)







Leave a Reply