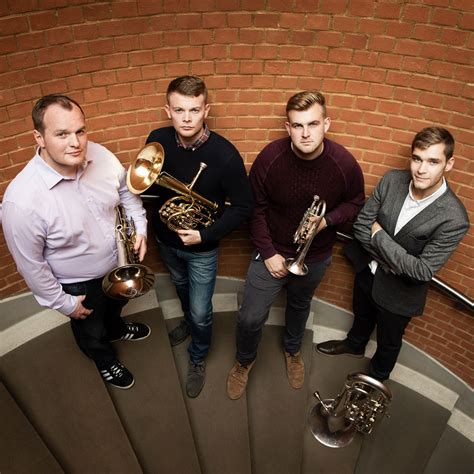
Meaning of Brass Instruments in Music
Brass instruments are a group of wind instruments that are typically characterized by their construction from brass or other metals. These instruments produce sound through the vibration of the player's lips against a cup- or funnel-shaped mouthpiece, which causes the initial vibration of an air column. The vibration of the air column inside the instrument creates sound waves that resonate and produce musical tones. The brass family of instruments includes instruments such as the trumpet, trombone, French horn, and tuba .
The term "brass instrument" is primarily defined by the way the sound is produced, rather than the material from which the instrument is made. While most brass instruments are made of brass or other metals, there are also examples of brass instruments made from wood, such as the alphorn, cornet, serpent, and didgeridoo. Conversely, some woodwind instruments, like the saxophone, are made of brass.
Brass instruments are known for their ability to produce loud and powerful sounds, making them well-suited for playing in orchestras and other musical ensembles. Their distinctive sound and versatility have made them popular in various genres of music, including classical, jazz, pop, and marching bands
The family of wind instruments which are made of a brass or silver tube (either cylindrical bore or conical bore) that flares into a bell at the end, have cupped mouthpieces similar to that of a trumpet, and usually have valves or slides. The members of this family include the trumpet, horn, trombone, tuba and their families.







Leave a Reply