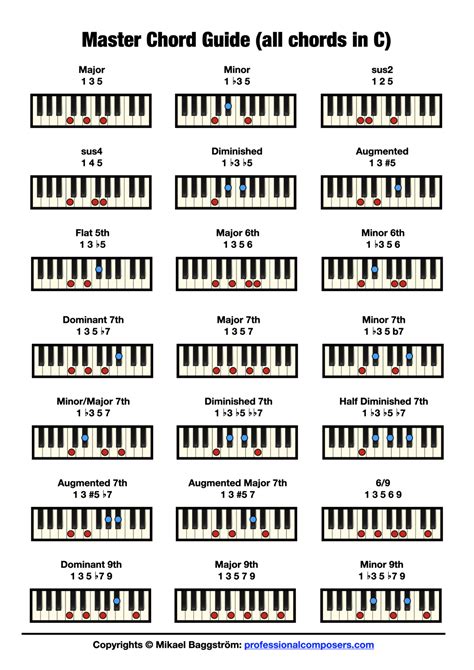
Ninth Chord in Music
A ninth chord in music is a chord that includes the ninth note of a scale in addition to the root, third, and seventh notes. It is a four-note chord that adds richness and complexity to a musical composition. The ninth note is typically added above the octave, which gives the chord its distinctive sound.
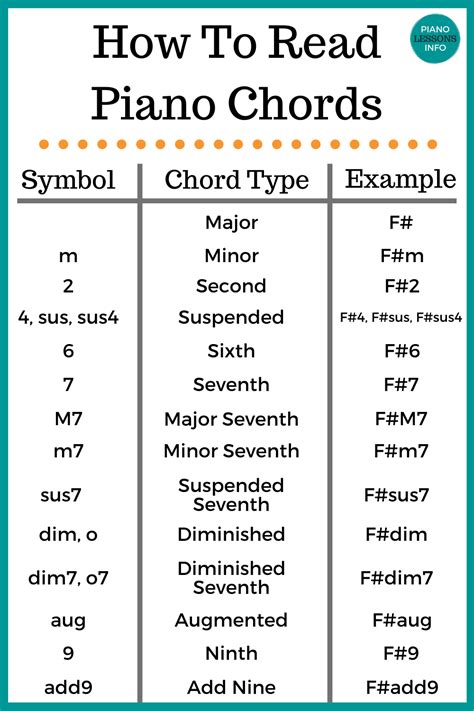
There are different types of ninth chords, including dominant ninth (9), major ninth (M9), and minor ninth (m9) chords. The dominant ninth chord is the most common type and consists of a dominant seventh chord with an added major or minor ninth. For example, a dominant ninth chord in the key of C would include the notes C, E, G, B, and D. The major ninth chord is formed by adding a major ninth to a major seventh chord, while the minor ninth chord adds a minor ninth to a minor seventh chord.
Ninth chords are often used in jazz and popular music to add color and tension to a composition. They can create a sense of drama and enhance the emotional impact of a musical piece. In Schubert's "Erlkönig," for example, the dissonant voicing of a dominant minor ninth chord is used to heighten the sense of threat and tension.
It's worth noting that ninth chords do not typically include the eleventh or thirteenth notes of a scale The ninth chord is primarily focused on the root, third, seventh, and ninth notes.
Overall, ninth chords are a versatile and expressive tool in music composition, adding depth and complexity to harmonic progressions and melodies.
A chord having usually, but not necessarily, five tones, the interval between the base note and the highest note being a ninth. The other notes in the chord would be the root, third, fifth, and seventh. In the C chord below, the root is C, the third is E, the fifth is G, the seventh is B, and the ninth is D.






Leave a Reply