Meaning of Meter in Music
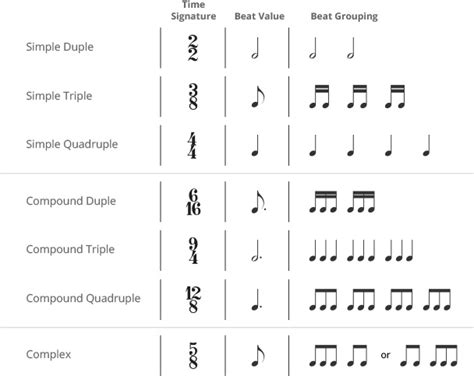
In music, **meter** refers to the rhythmic pattern created by the grouping of beats into regular measures or bars. It is the organization of beats in a piece of music. The meter is indicated by a time signature at the beginning of the music, which specifies the number of beats in a measure and the value of the basic beat. For example, a 3/4 meter has three quarter-note beats per measure.
The meter of a piece of music establishes a repetitive pattern of strong and weak beats, providing a framework for the rhythms within the music. While the rhythms themselves may not be repetitive, they suggest a repeated pattern of pulses. The beat of the music, which you tap your foot to or clap your hands with, is based on these pulses.
Different meters are categorized as simple or compound. Simple meters are duple (e.g., 2/2, 2/4), triple (3/4,
Measure of time; arrangement of poetical feet; the grouping of beats into regular patterns. The organization of the rhythmic patterns in a composition are done in such a way that a regular, repeating pulse of beats may continue throughout the composition.
In addition, you can familiarize yourself with the terms:
- [British] metre







Leave a Reply